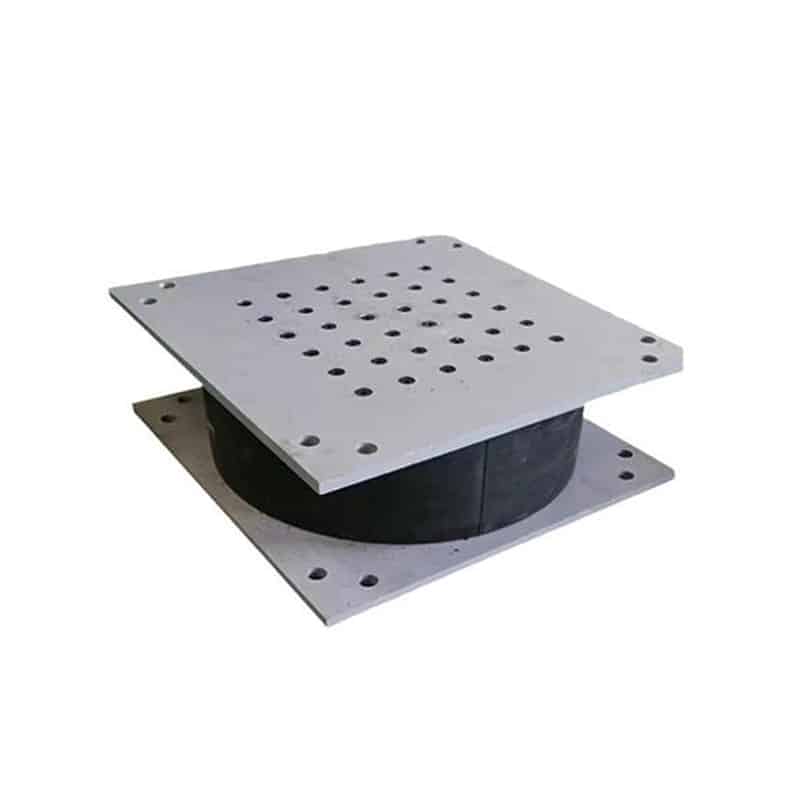
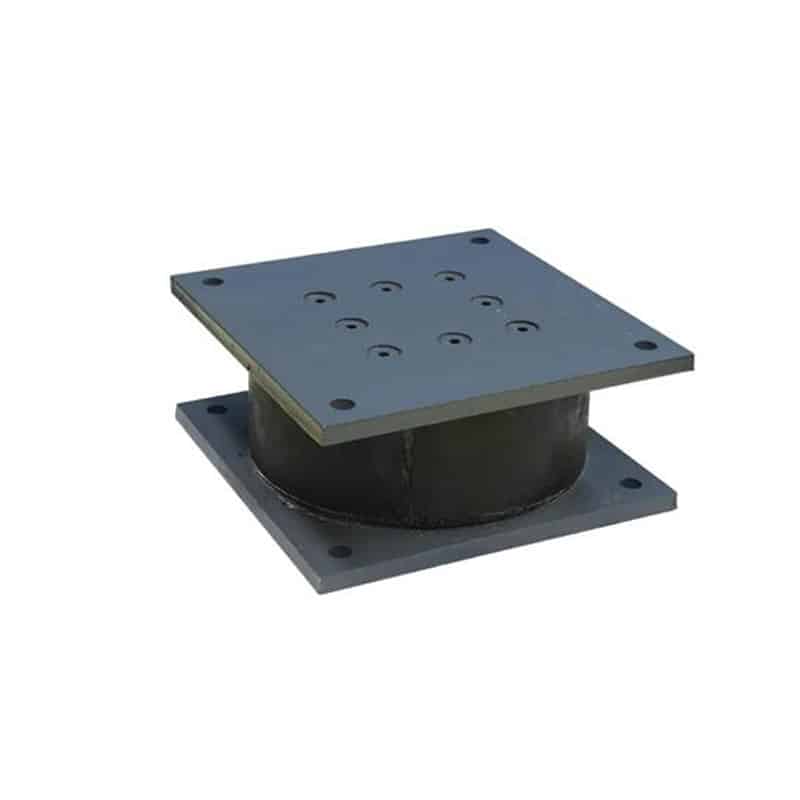
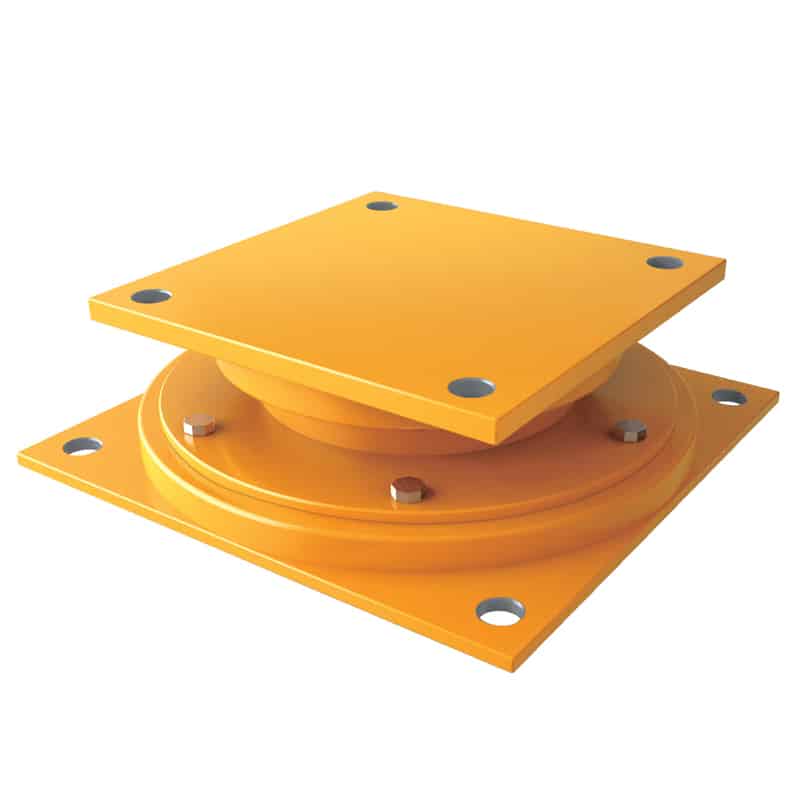
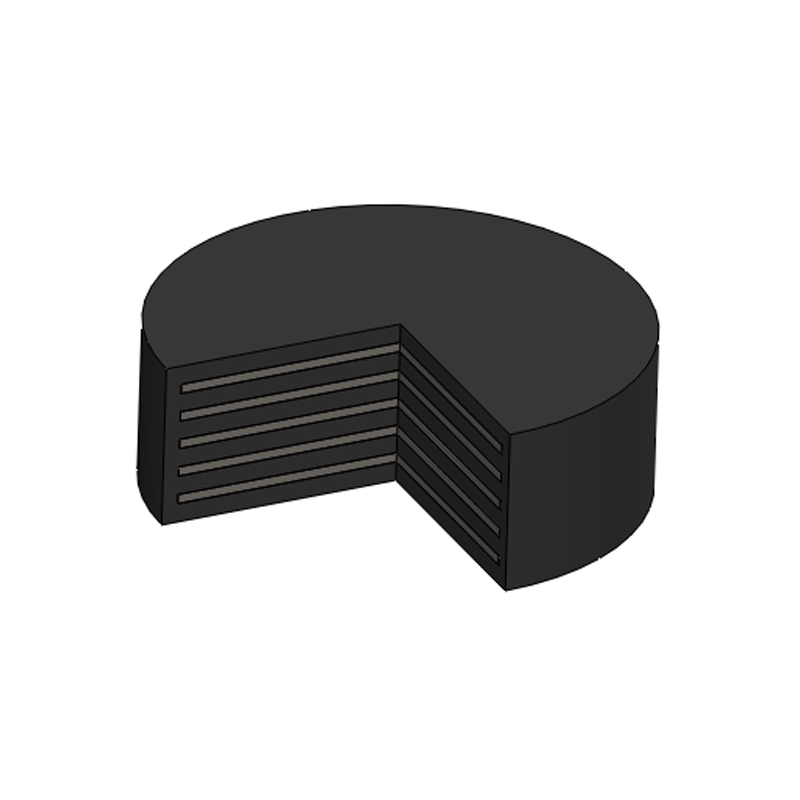
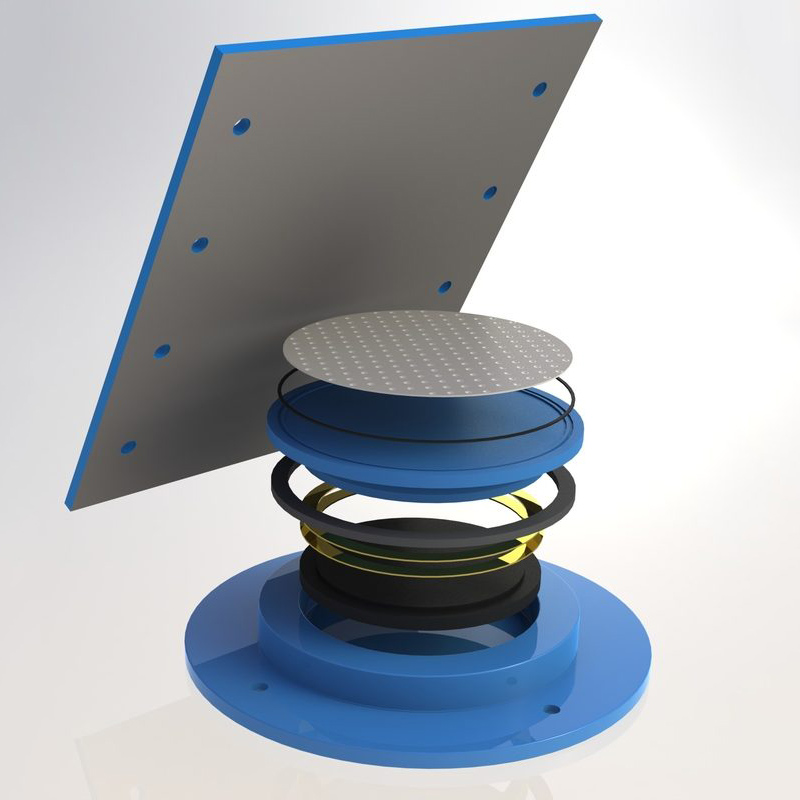
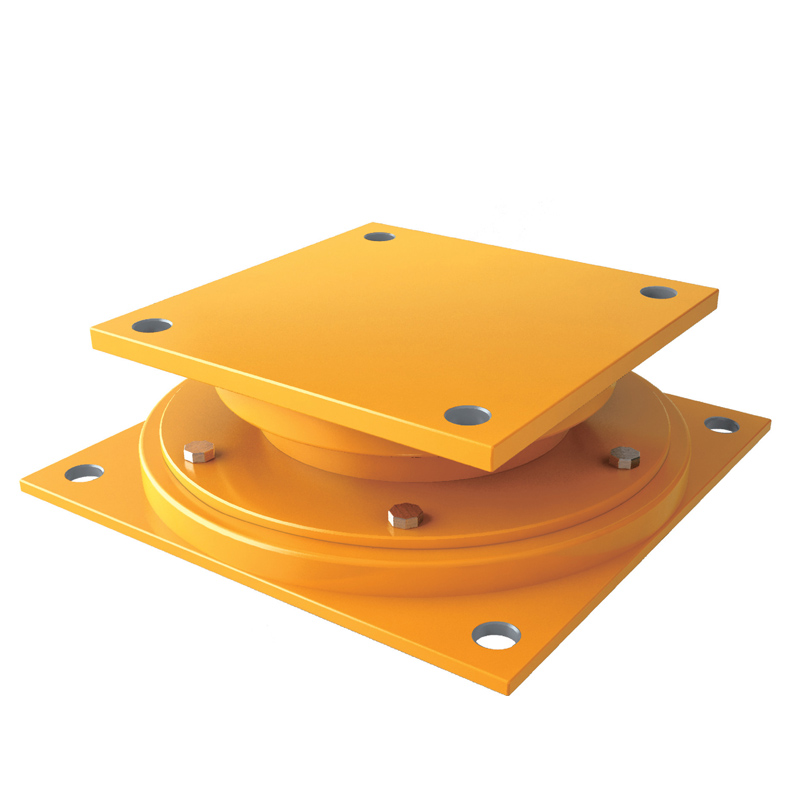
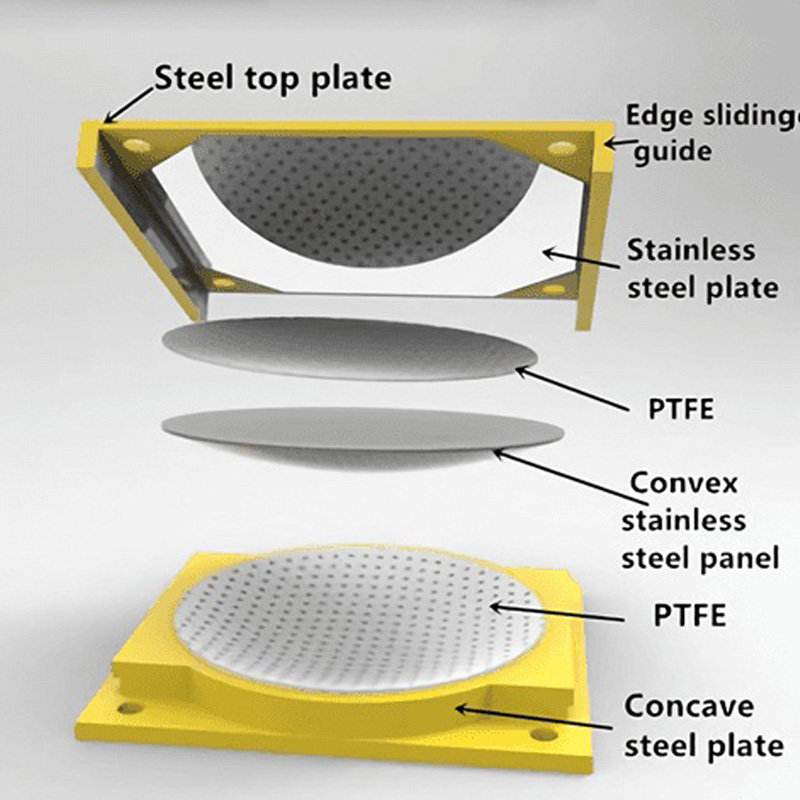
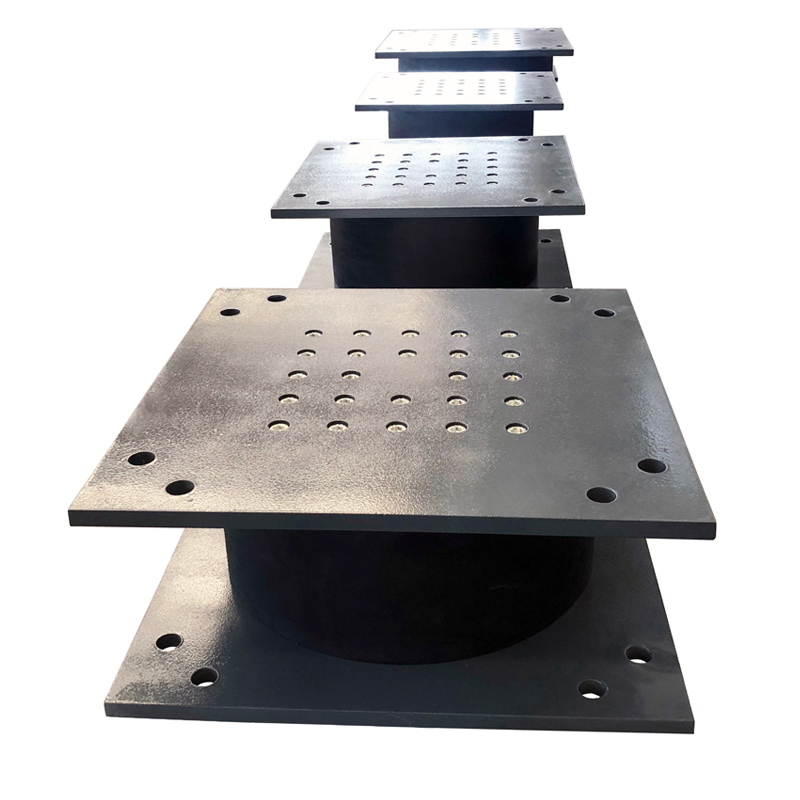
An elastomeric bearing is a type of structural support device used in construction and engineering to allow movement and absorb stress in structures, particularly bridges and buildings. Made from layers of elastomeric materials (like rubber) and often reinforced with steel plates, these bearings provide flexibility, allowing for vertical and horizontal movement due to thermal expansion, seismic activity, or other forces.
HomeCategory
BRIDGE BEARINGS AND SEISMIC DEVICES
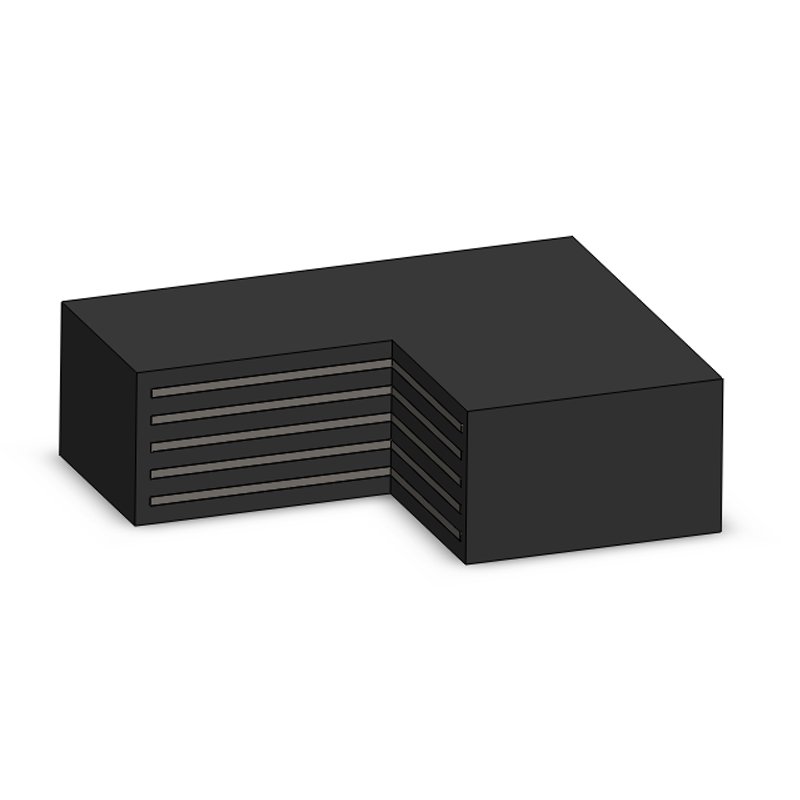
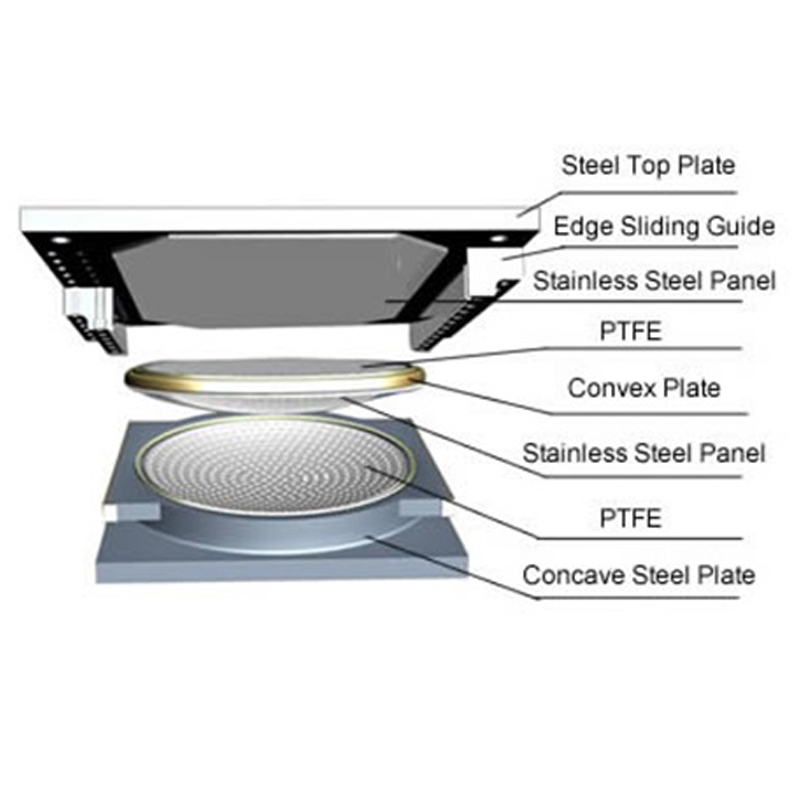
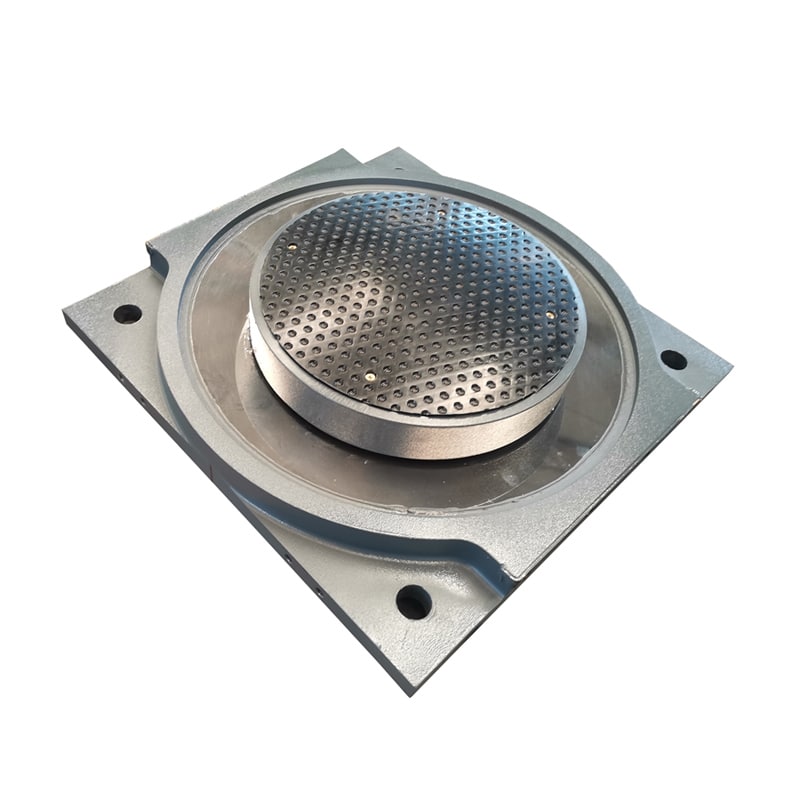
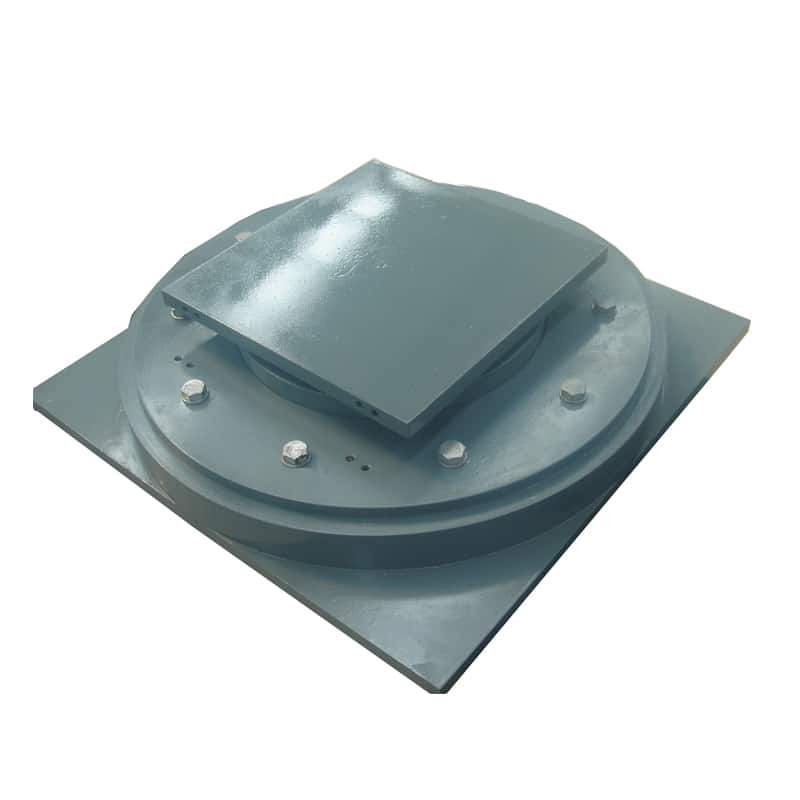
A pot bearing is a type of structural bearing used to support loads while allowing for rotational and translational movements. It consists of a cylindrical pot filled with elastomeric material or a sliding surface, typically made of steel or PTFE, which helps accommodate movements due to thermal expansion, settlement, or seismic activity.
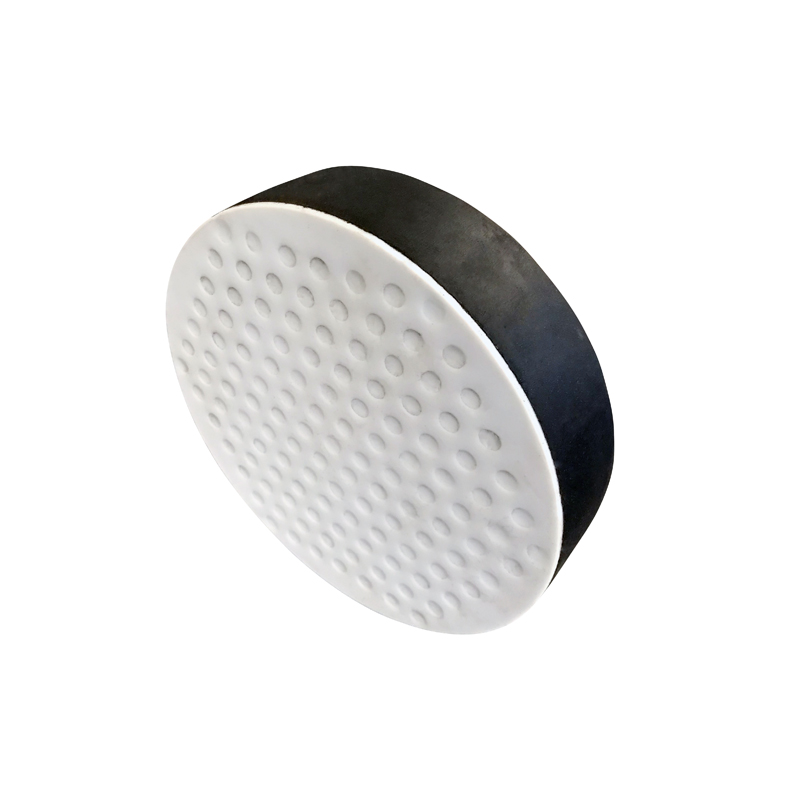
A spherical bearing is a type of bearing designed to allow for angular movement between two connected components while supporting radial loads. It consists of a spherical outer surface that fits into a matching housing and an inner race, allowing for rotation and tilting.
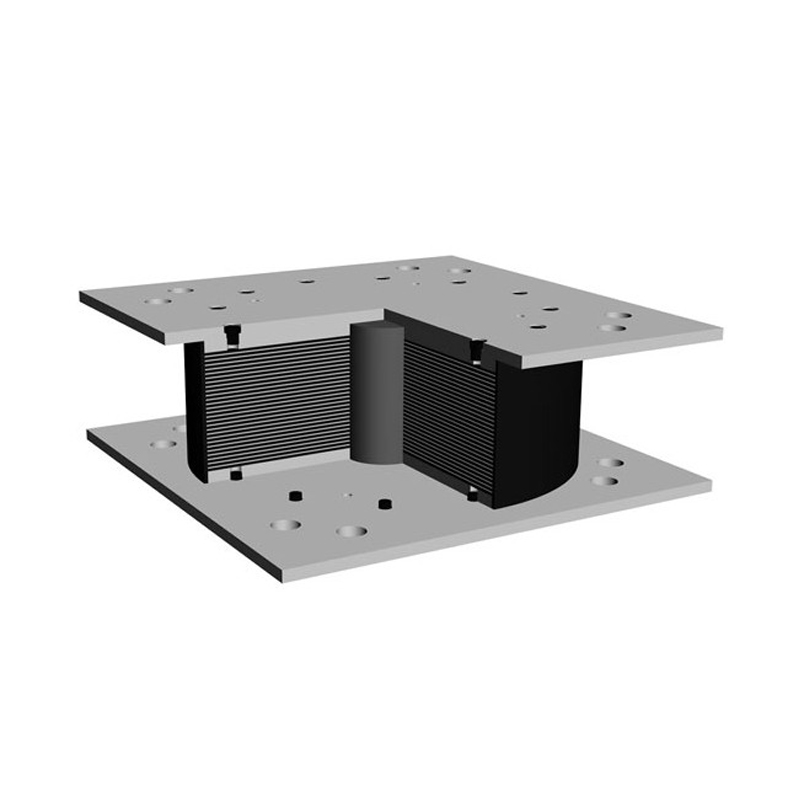
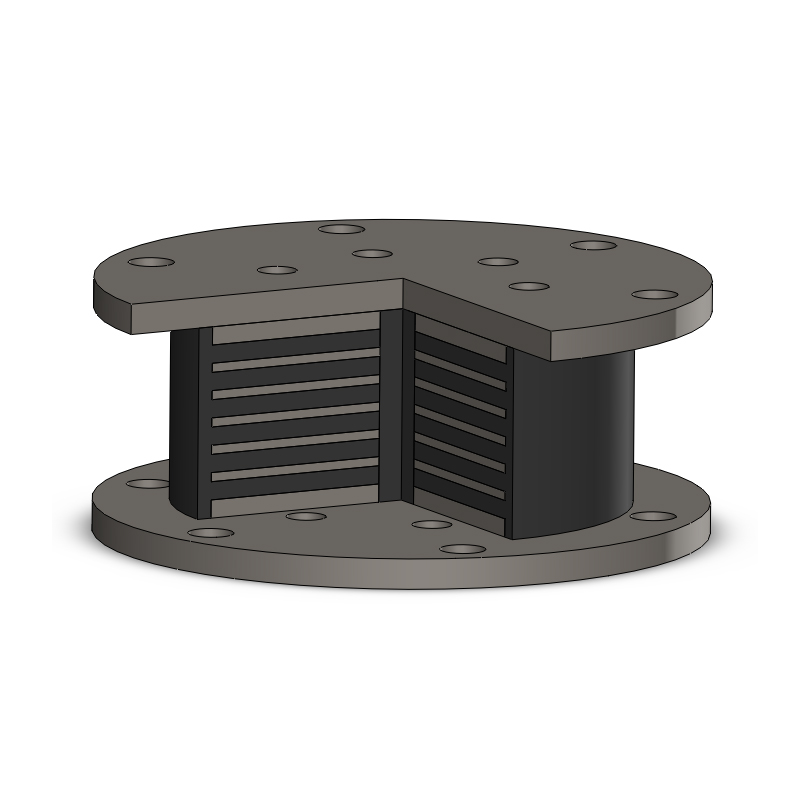
LRB, or Lead Rubber Bearing, is a type of elastomeric bearing designed specifically for seismic applications. It combines layers of rubber with a lead core to provide both flexibility and damping properties. Here are its key features and applications:
LNR rubber bearings, often used in construction and engineering, are a type of elastomeric bearing designed to accommodate movements and vibrations in structures. They are typically made of layers of rubber and steel, providing flexibility and strength.
A pendulum bearing is a type of bearing designed to accommodate both vertical and horizontal movements while providing rotational flexibility. It typically features a spherical or cylindrical shape, allowing it to pivot or swing like a pendulum, which is ideal for structures subject to dynamic forces.
A viscous fluid damper is a device that dissipates energy through the movement of a viscous fluid, typically used to reduce vibrations and control motion in various engineering applications.
The BRB (Base Isolation Bearing) system is a seismic protection technology used to enhance the resilience of structures during earthquakes. It works by decoupling the building from ground motion, allowing it to move independently from the seismic forces.